Elk hunting in America, especially in the American West, demands far more preparation than a typical North American deer hunt.
Unlike other types of deer, an elk hunt typically entails trekking through rugged backcountry, weathering unpredictable conditions, and lugging heavy loads.
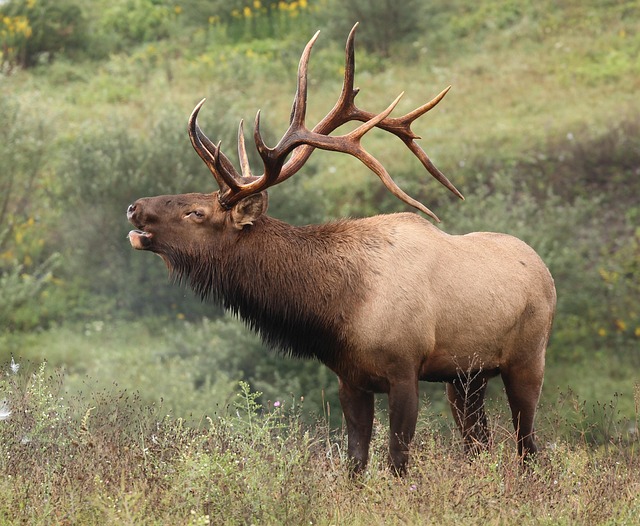

Read on as we cover everything from what to pack for your elk hunt, to how to carry it safely, and best practices for getting any game meat out of the field.
Whether you’re just heading out for a day hunt or embarking on a multi-day expedition, your gear and preparation can make or break you.
For that reason, we thought it crucial to outline some of the basics and essential equipment every elk hunter needs, as well as some of the preparation and gear you might have never even thought of.
Elk Hunting Pack List And Gear Essentials (Day/Short Hunts)
On the simpler side of things, day hunts will usually kick off before dawn and may not come to an end until well after dark.
Even though you’re not overnighting, elk country is vast, remote, and often brutal, so packing smart is key.
A 1,500–3,000 cubic inch daypack with load lifters and a solid hip belt is a great starting place. Many frame-style daypacks can also haul a quarter if needed, giving you the meat-hauling capacity you need, even on a single-day hunt.

Layering is Critical
Starting at your base layer, wear a moisture-wicking base followed by an insulating mid-layer like fleece or a puffy, and then finish with a waterproof, breathable shell.
Mountain weather changes quickly, and you will find yourself in the mountains for most elk hunts, so always bring rain gear, even if it appears to be a clear day.
A beanie or brimmed hat, light gloves, and extra socks are also highly recommended. Now, when it comes to regulations, some states require rifle hunters to wear blaze orange, at minimum a vest and hat over your camo.
Footwear Matters, A Lot
On an elk hunt, hiking boots matter… a lot!
It is far easier to wear broken-in boots that are waterproof and that have ankle support. Do what you can to avoid breaking in new boots on an elk hunt.
You can also pair your broken-in boots with some warm wool or synthetic socks, just make sure to always pack a second pair. Trust us, it’s better to carry an extra pair back with you than to be stuck trying to hike with soaked socks if push comes to shove.

Be sure to pack a small foot care kit with moleskin, tape, blister pads, and foot powder. These kits are super light and do not add much weight to your pack, but if you for some reason need it, you do not want to be caught without it.
Navigational Needs
Bring a GPS or smartphone mapping app (with offline maps), plus a topo map and compass. If you are out on a guided elk hunt with an outfitter, there is a good chance they will have this covered.
A headlamp is another non-negotiable piece of gear for hikes in and out in the dark, so just make sure to carry spare batteries. Beyond extra batteries, there is a wide array of emergency gear that you should include, such as a fire starter, a small emergency blanket, and a basic first aid kit with personal meds.
Optics Can Make or Break You
Add chest-mounted 8x or 10x binoculars to your elk hunting pack list so you can constantly scan, especially in areas of thick timber.

There’s no point in trekking out to elk country if you cannot pick out an elk along the mountainside. So, good optics are a must!
A rangefinder is also extremely helpful, as elk may look closer than they are across canyons or open hillsides. This is especially true for bowhunters who rely on precise yardage. A lens cloth is also a plus.
Locked and Loaded
If you’re rifle hunting, be sure to clean and zero your firearm before the trip. Any time spent on the hunt prepping your rifle is time lost hunting elk. Just in case, pack a multi-tool or Allen wrench for field repairs.
Extra ammo or arrows are another obvious must-have. While it goes without saying for bow hunters, rifle hunters can also benefit from elk calls, so it can’t hurt to pack one.
Mind the Wind

If you hope to harvest an elk, scent control and wind direction is key…
Do your best to start with clean, unscented gear and make an effort to control scent in the field, elk have an amazing sense of smell.
More importantly, play the wind. A small chalk-based wind checker or milkweed fluff are perfect for reading air currents. At the end of the day, staying downwind is more important than any scent eliminator.
Processing gear
Don’t short yourself when it comes to processing gear:
- Sharp knife (or two, replaceable knife types are popular for processing)
- Knife sharpener
- Gloves
- Game bags
- Paracord
- Tarp or contractor bag (to keep meat clean)
If you prefer traditional field dressing, add a bone saw or small hatchet, but the gutless method saves weight.
Also, don’t forget zip ties or tape and a pen to attach your tag per state law.
Food and Hydration

Water is a crucial part of any elk hunting pack list. Even a day hunt requires 2–3 liters of water.
A hydration bladder is your best bet when it comes to saving space and weight.
In dry zones, a compact filter or purification tablets are a great backup that can save your hunt.
Eat before heading out and pack light snacks like jerky, trail mix, nuts, and energy bars. Freeze-dried meals and MRI-style meals are great for longer sits, just again, mind the smell. Electrolyte packets are another nice touch to help replace salts lost on big climbs.
Finish Your Kit
Some miscellaneous gear you should keep in mind is toilet paper in a zip bag, emergency duct tape (wrapped around a water bottle or trekking pole), and extra waterproof storage for your license and tags.
In bear country, bear spray is always a plus, as it can often be more effective than a sidearm.
Some hunters use trekking poles, which can save your knees on steep descents or when hauling meat, but this is not very common.
-
N1 Outdoors® Tine Lines™ Elk Antler Tee
Price range: $26.99 through $29.99 -
N1 Outdoors® Tine Lines™ Whitetail Deer Antler Tee
Price range: $26.99 through $29.99 -
N1 Outdoors® “Outdoor Npressions™” Boot Print Tee
Price range: $24.99 through $28.99
Elk Hunting Pack List And Multi-Day Backcountry Gear (Extended Hunts)
If a day hunt is the equivalent of a long hike, a multi-day elk hunt is like a full-blown camping trip.
Multi-day elk hunts call for all of the same gear as a day-hunt, plus everything you need to survive for several days in the backcountry.
You’ll be hiking miles from any road, so self-reliance is critical. You’ll likely need a 4,000–7,000 cubic-inch internal or external frame pack with a strong meat shelf.
Make sure you know how to cinch loads and practice packing quarters as well. You’ll need to keep your total pack weight below one-third of your body weight, usually around 40–60 pounds, so that you’re not completely burned out before the hunt even begins.
Shelter Options
A multi-day hunt calls for either a one or two-person tent, bivy sacks, or hammocks (with a rainfly).
Make sure to bring a setup with strong weather protection. A ground tarp is also a must-have to protect your tent floor and to use as a dry surface for gear or meat processing.
The best practice for sleeping bags is being rated at least 10°F colder than the lowest expected temps, as mountain nights can fluctuate heavily and drop below freezing, even in early Fall.

Down bags are great and much lighter, but keep in mind that they need to stay dry, whereas synthetics work even when wet.
Whichever you go with, an insulated sleeping pad is a great addition to keep warm in your tent and off the cold ground.
Modular Clothing
Be prepared to wear your main hunting outfit for several days. Make sure to also pack:
- An extra set of underwear
- An extra set of base layers
- Additional socks
- A second insulating layer (if in a region where conditions might turn frigid)
- Rain gear (especially in the rainier seasons)
In early archery seasons, sun protection is another essential, so use UPF-rated clothing and sunscreen.
Lastly, camp shoes are a huge plus to let your feet breathe after a long day in boots.
Planned Meals
Pre-packed and labeled food in zip or vacuum sealed bags is best.
Freeze-dried dinners are great because they are lightweight, nutritious, and only require boiling water. Good breakfast options might be oatmeal, granola, or just energy bars.

For lunch and snacks, rely on no-cook, high-calorie options like peanut butter crackers/tortillas, jerky, trail mix, cheese, and dried fruit.
Aim high for 3,000–4,500 calories per day, you’ll be pushing yourself on the hunt.
A compact canister stove, fuel, titanium pot, lighter, long spoon, and insulated mug cover should cover just about everything else you need, and unless you’re crazy, some instant coffee or energy drink mixes are a must-have.
Hydration is Critical
Locate reliable water sources like creeks or springs using maps or GPS apps.
Use a pump, gravity, or squeeze filter, and always carry tablets as backup. Store 3–4 liters in camp and 2+ liters when you’re on the move.
Camel up. Drink a full liter before leaving a water source to lighten your load. In late-season hunts, make sure to keep freezing risks in mind with bladders, in which case bottles may be the better option.
Navigation and Communication
GPS and communication become far more important when spending several days in the backcountry.

Pack a GPS and compass, plus a paper map. Bring spare batteries or a power bank for recharging your headlamp, GPS, and phone.
Keep in mind that cold kills batteries fast, so keep electronics close to your body at night. A satellite messenger like a Garmin inReach can also send SOS signals and text family from anywhere in case of emergency.
Radios are also helpful for in-field communication with hunting partners to better coordinate stalks and to stay safe.
Fire Essentials
Waterproof matches, a lighter, and fire cubes or magnesium strikers are all perfect as backup firestarters. Another situation you do not want to find yourself in is being stuck at camp without a way to start a fire.
Extended First Aid Kit
Your kit needs to cover more than just cuts:
- Ibuprofen
- Allergy pills
- Anti-diarrheal tablets
- Antibiotic ointment
- Gauze
- Medical Tape
- Blister care.
Also include any personal medications (split between your pack and pocket). Safety pins and zip ties, while strange, can be extremely useful for gear and medical fixes.
Preserving Your Elk Meat
Hang your game bags in shaded areas with good airflow, and keep them off the ground.
Prioritize loins and quarters if warm weather limits how much you can pack. If possible, you might need to make more than one trip, so don’t try to carry everything at once.
Just work with your group to hoist the packs and mark any meat caches with GPS and flagging tape.
Miscellaneous Camp Items
While keeping pack weight down is a must, there are some miscellaneous camp items that just make life easier.

Small LED lanterns or dimmed headlamps are great for your tent and extra cordage is good for drying gear or rigging up tarps.
A trowel is also great for waste disposal unless you’re using WAG bags. Other hygiene products like wipes, toothbrush, toothpaste, and a tiny bottle of biodegradable soap can make all the difference as well.
Just make sure to store toiletries and food well away from camp, preferably hung up, to avoid any unwanted visitors in the middle of the night.
Advanced Extras
Beyond what we’ve covered, you can always bring a GPS watch to track your elevation, time, and distance into the hunt, all of which help pace and mark spots.
For long glassing sessions, consider a spotting scope and tripod, but only bring it if you’ll actually use it. Every ounce counts when out in the backcountry.
Hunt Smart, Pack Smarter
Your pack list and gear prep shouldn’t be about packing as much as you can, but rather making sure you’re ready for everything from early-morning hikes to hauling meat at dusk with the least amount of gear possible.

Skill only takes you so far when it comes to elk hunting. Every hunt is only as successful as the preparation.
Use this information as a baseline and refine it based on your exact hunt, as no two trips are the same.
As you become a seasoned elk hunter, each trip will teach you what works and what doesn’t. What matters is that you stay safe and enjoy the grind.
There are very few things that match the feeling of bringing home a trophy elk after days of hard-earned effort, so give yourself the best shot you can and prepare yourself for the hunt the best you can!