Saltwater fish have long been a favorite for seafood enthusiasts, due to their distinct flavors and wide availability. Whether grilled, baked, or fried, these fish offer a range of tastes that can satisfy any palate.
In this article, we’ll explore the top 10 best-tasting saltwater fish, discussing their unique qualities and where in the world they can be found and fished for.
Best Tasting Saltwater Fish (The Top 10)
Now let’s move on to the top 10 list, where each selection brings something special to the table in terms of flavor and cooking versatility.
1. Mahi-Mahi (Dolphinfish)
Mahi-Mahi tops our list for its mild and slightly sweet flavor, which is often compared to that of swordfish but with a more tender texture. This fish is not only delicious, but also versatile in the kitchen, lending itself well to various cooking methods such as grilling, broiling, and baking. Its firm, lean meat holds up well to different seasonings, making it a popular choice for fish tacos and seafood dishes that require a robust flavor.
Where to Catch Mahi-Mahi
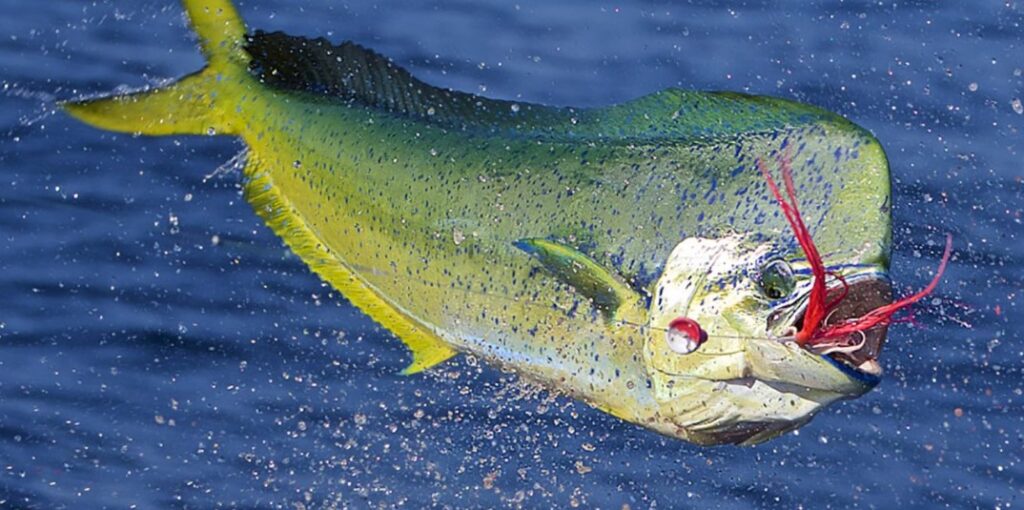

Mahi-Mahi is typically found in warm waters, especially in the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean, and off the coast of Hawaii. Anglers can often find mahi-mahi near floating debris or seaweed patches, where they often gather in schools (photo credit: Sol Y Mar Magazine).
2. Yellowfin Tuna (Ahi)
Yellowfin Tuna, or Ahi, is celebrated for its rich, meaty texture and mild flavor. This fish is a favorite for sushi and sashimi lovers due to its delicate taste when served raw.

When cooked, Ahi retains a steak-like quality, making it ideal for searing or grilling. Its versatility and firm flesh make it a top choice among chefs and home cooks alike.
Where to Catch Yellowfin Tuna

Yellowfin tuna is widely revered for its rich flavor and mild flavor.
This species is found in tropical and subtropical oceans around the world, particularly in the Pacific and Indian Oceans. Anglers often pursue Yellowfin Tuna during deep-sea fishing expeditions.
3. Red Snapper
Red Snapper is renowned for its sweet, nutty flavor and tender texture. This fish is highly versatile and can be prepared in various ways, including grilling, baking, and frying. Its mild flavor pairs well with a wide range of seasonings and sauces, making it a popular choice for both casual and gourmet dishes.
Where to Catch Red Snapper

Red snapper is appreciated for its preparation versatility, having a sweet flavor and tender texture.
Red Snapper is commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico and along the southeastern coast of the United States. They are typically caught in deeper waters near reefs and shipwrecks.
4. Halibut
Halibut is prized for its mild, sweet taste and firm, flaky texture. This fish has a low oil content, making it a leaner option that still delivers a satisfying flavor. Halibut is versatile in the kitchen and suitable for grilling, broiling, and baking. Its firm texture allows it to hold its shape during cooking, making it a reliable choice for a variety of dishes.
Where to Catch Halibut

Halibut is primarily found in the cold waters of the North Pacific, particularly off the coasts of Alaska, Canada, and Russia. Fishing for halibut is often done at great depths, where these large fish thrive.
5. Sea Bass
Sea Bass is celebrated for its delicate, buttery flavor and tender, flaky flesh. This fish is a favorite in fine dining, where it is often paired with light sauces and subtle seasonings to enhance its natural taste. Sea Bass is also a versatile fish, suitable for steaming, grilling, or baking.
Where to Catch Sea Bass
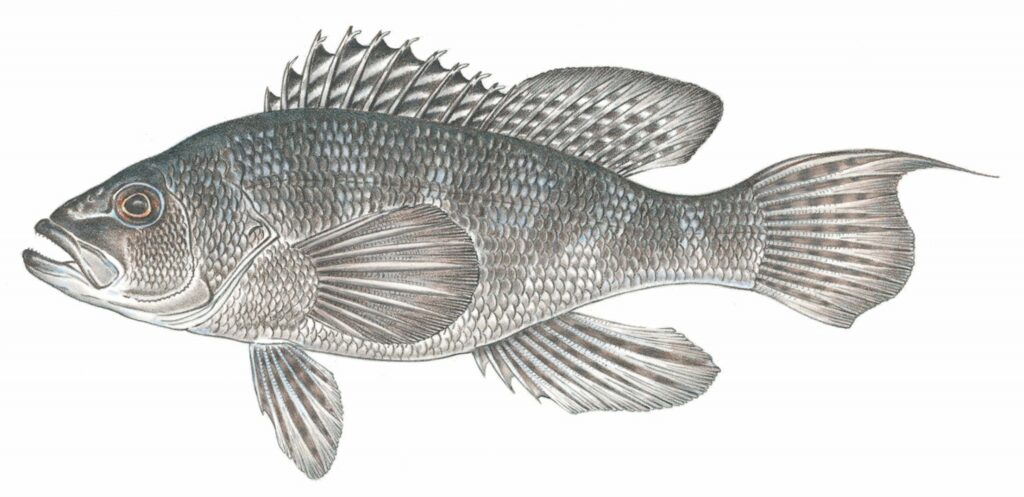
Sea Bass is commonly found in the Atlantic Ocean, particularly along the coasts of the northeastern United States and Europe. They are often caught near the ocean floor, around reefs, and rocky outcrops (photo credit massogov.)
6. Grouper
Grouper is known for its mild flavor and firm yet moist texture. This fish has a slightly sweet taste that pairs well with a variety of seasonings, making it a versatile option for many dishes. Grouper is especially popular for grilling, as its firm flesh holds up well over high heat.
Where to Catch Grouper

Grouper is commonly found in the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean, and the southeastern coast of the United States. They are often caught near reefs, wrecks, and other underwater structures.
7. Swordfish

Swordfish is a meaty fish with a mildly sweet flavor that is often compared to that of tuna. Its firm texture makes it ideal for grilling, and it is often served as a steak due to its thick, hearty fillets. Swordfish is also versatile and suitable for baking, broiling, and even sashimi.
Where to Catch Swordfish

Swordfish are typically found in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Mediterranean Oceans. They are deep-sea fish, often caught using longline fishing methods.
>> More of the best fishing rod wraps HERE!
8. Salmon
While more commonly associated with freshwater, many species of Salmon, such as the Atlantic Salmon, spend a significant portion of their lives in saltwater. Salmon is beloved for its rich, oily flesh and distinct flavor, which can range from mild to robust depending on the species.

Salmon is an incredibly versatile fish and can be smoked, grilled, baked, or poached.
Where to Catch Salmon

Atlantic Salmon is found in the northern Atlantic Ocean, while Pacific species are found along the coasts of Alaska, Canada, and Russia. Salmon fishing often occurs in both saltwater and freshwater environments, as these fish migrate upstream to spawn.
9. Wahoo

Wahoo is a lesser-known but highly prized fish for its delicate, slightly sweet flavor and firm, white flesh. This fish is often compared to Mahi-Mahi and Tuna, offering a similar taste profile but with a leaner texture. Wahoo is excellent for grilling, broiling, and searing.
Where to Catch Wahoo
Wahoo is found in tropical and subtropical waters worldwide, including the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. They are often caught during offshore fishing trips, particularly around floating debris.
10. Flounder

Flounder is often pan-fried, baked, or stuffed, making it a versatile option for many seafood dishes.
Flounder is a mild, sweet-tasting fish with a delicate, flaky texture. Its subtle flavor makes it an excellent canvas for various seasonings and cooking methods.
Where to Catch Flounder
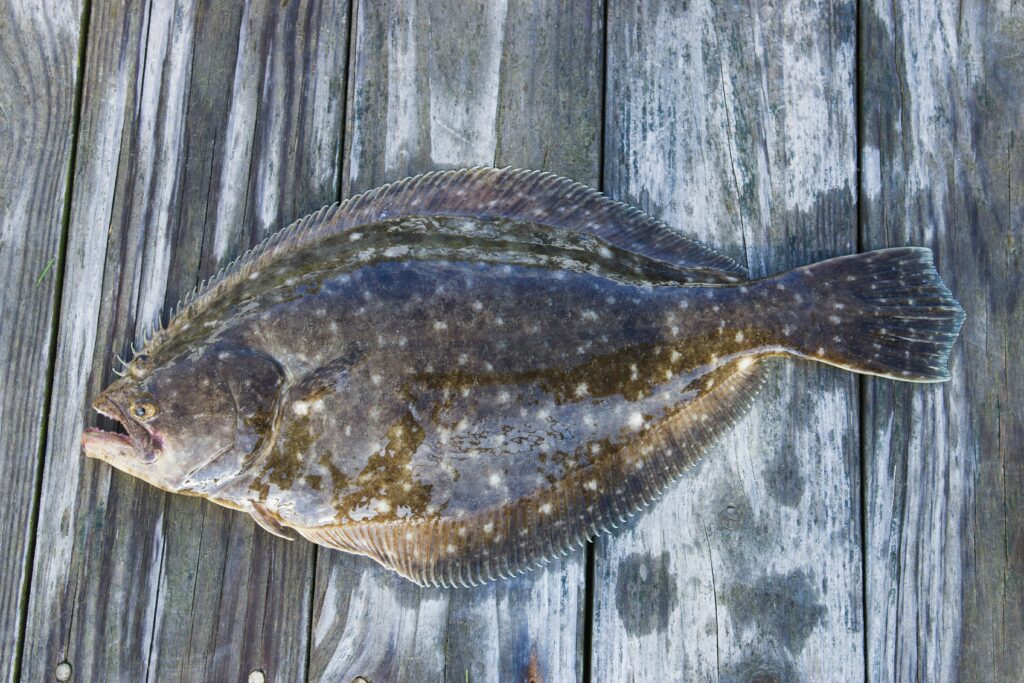

Flounder, as well as halibut have a unique, flat body structure.
Flounder is commonly found along the Atlantic and Gulf coasts of the United States, particularly in shallow waters near the shore. They are often caught by bottom fishing or using nets.
Honorable Mention: Barramundi
Although Barramundi just missed our top 10, is still worth considering for its taste and texture. Barramundi certainly deserves an honorable mention for its mild, buttery flavor and moist, firm texture. This fish is highly versatile and is often compared to Sea Bass and Snapper. Barramundi is a great choice for grilling, baking, or frying, and it pairs well with a variety of seasonings and sauces.
Where to Catch Barramundi

Barramundi is native to the Indo-Pacific region, particularly in the waters of Australia, Southeast Asia, and India.
For those interested in catching this fish, a comprehensive guide to Barramundi fishing can be incredibly helpful, especially considering its popularity and the sustainable fishing practices often employed. Barramundi is also frequently farmed, making it accessible in various regions.
Final Thoughts On Best Tasting Saltwater Fish
The saltwater fish covered above represent some of the best tasting fish options available for seafood enthusiasts. Each offers a unique flavor profile and texture, making them suitable for various culinary applications.
So, whether you’re an experienced angler looking to catch your next meal or a home cook seeking new fish to try, this list provides a comprehensive guide to some of the most delicious saltwater fish. With such diverse flavors and qualities, there’s a fish on this list to suit every taste.






















